Title
- Mini-topic: External Sort-Merge Algorithm (Page 701)
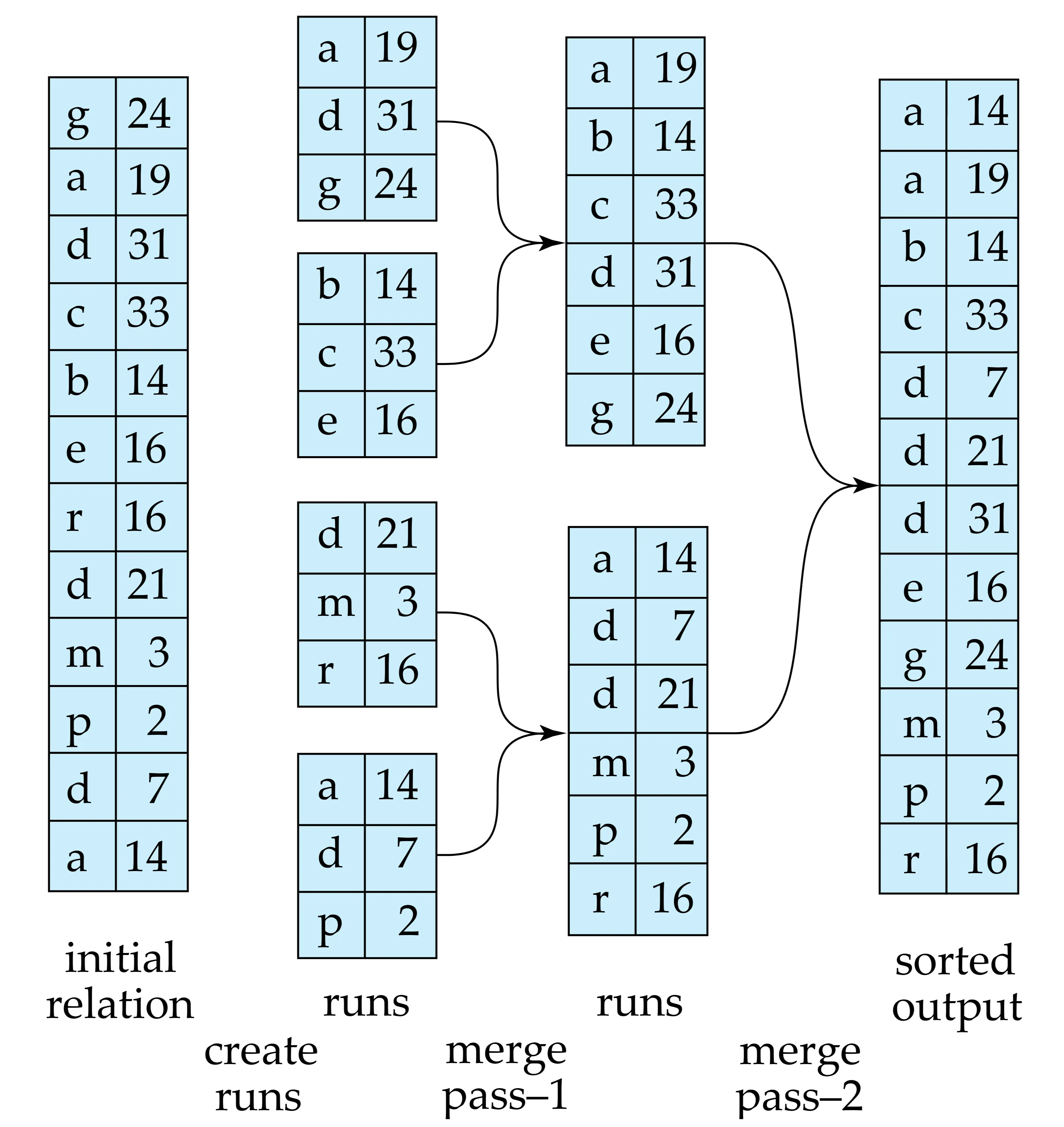
- Micro-topic: Figure 15.4 External sorting using sort-merge. (Page 703)
- Mini-topic: Cost Analysis of External Sort-Merge (Page 702)
External Sort-Merge Algorithm (Page 701)
The External Sort-Merge Algorithm is the most common technique for sorting relations that don’t fit in memory. It works in two main stages:
-
Run Creation Stage:
- Read
Mblocks of the relation into memory (whereMis the number of available memory blocks). - Sort the in-memory data using an efficient internal sorting algorithm (like quicksort).
- Write the sorted data (a “run”) to a temporary file on disk.
- Repeat until the entire relation is processed, creating multiple sorted runs (Ri).
- Read
-
Merge Stage:
- If Number of Run (N) ⇐ M, one pass merge is enough.
- If the number of runs (N) is less than or equal to M, merge them in a single pass using an N-way merge:
- Read one block from each run into memory buffers.
- Repeatedly find the smallest tuple among all buffers (considering the sort order).
- Write the smallest tuple to the output.
- If a buffer becomes empty, read the next block from the corresponding run (if any).
- If N > M, perform merge in multiple passes.
- If the number of runs is greater than M, perform multiple merge passes:
- Each pass merges at most
M-1runs (because one buffer block is for output). - Repeat passes until the number of runs is less than M.
- A final pass merges the remaining runs into the sorted result.
- Each pass merges at most
Example
Cost Analysis of External Sort-Merge (Page 702)
The cost of external sort-merge is dominated by disk I/O. We can estimate it as follows:
- br: Number of blocks containing the relation
r. - M: number of blocks in the main memory buffer available for sorting.
- bb number of blocks for buffering input run.
-
Run Creation:
- Reads every block and writes it out: block transfers.
- Number of initial runs:
-
Merge Stage:
- Each pass (except possibly the last) reads and writes every block.
- With each pass, number of runs decreases by factor of ().
- Number of merge passes (excluding last pass):
- Total number of block transfer except last pass =
-
Total Block Transfers:
-
Disk Seeks:
- Run generation phase:
- Each merge pass read input: seeks
- Each merge pass output, if on same disk: seeks.
- Total Seeks (excluding the final pass):