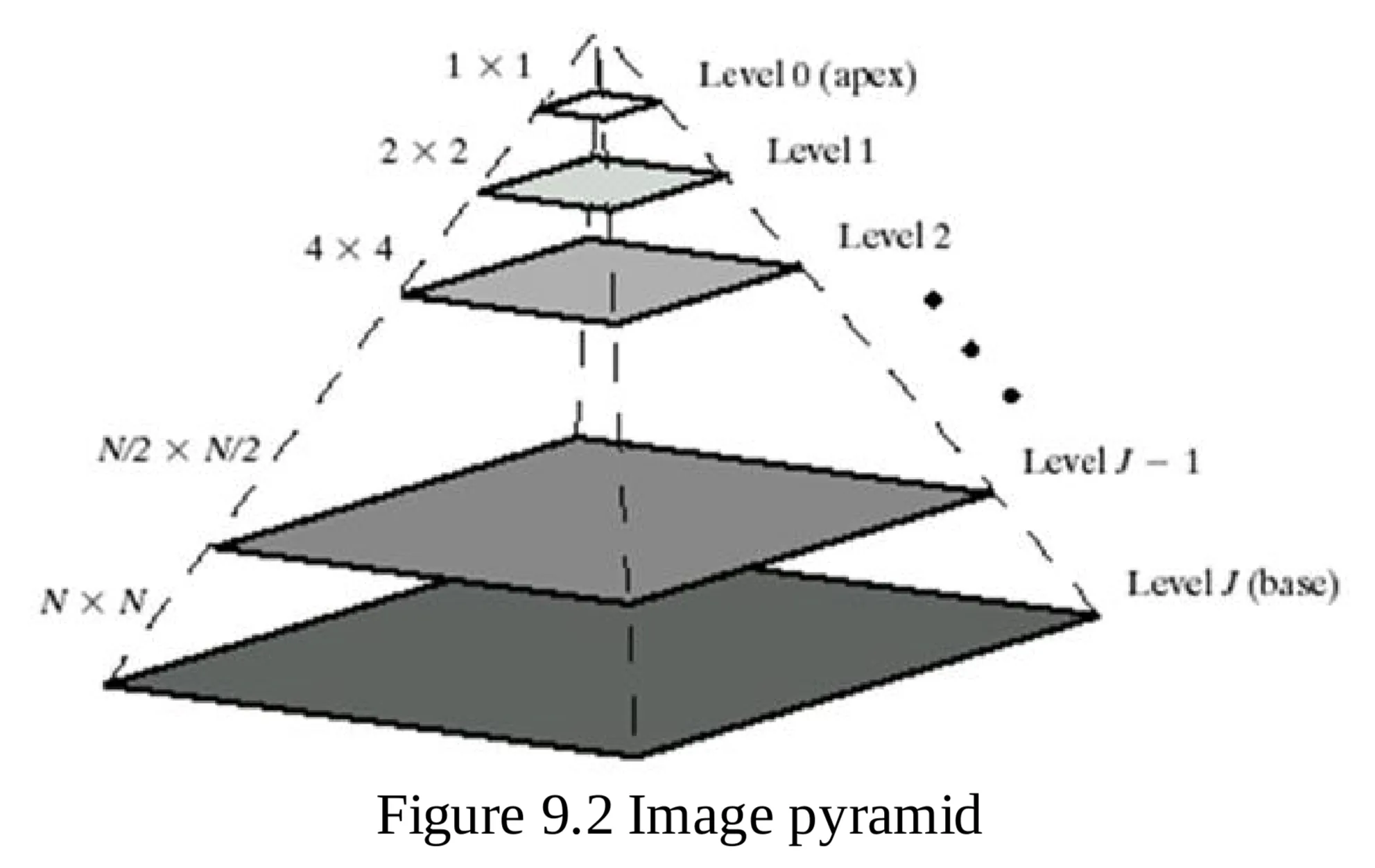
- Structure: Represent images at multiple resolutions. A collection of decreasing resolution images arranged in a pyramid shape.
- Highest Resolution: At the pyramid base (Level ).
- Resolution and Size: Decrease as you move up the pyramid.
- Base Level: Size .
- General Level size: , .
- Number of Pixels:
-
Building Image Pyramids (Iterative Process)
- Compute Reduced-Resolution Approximation: Filter and downsample (by a factor of 2) the level input image. Place the result at level of the approximation pyramid.
- Create Estimate of Level j Input: Upsample and filter the reduced resolution approximation from step 1. The resulting prediction image has the same dimensions as the level input.
- Compute Difference: Subtract the prediction image (step 2) from the input (step 1). Place the result in level of the prediction residual pyramid.
-
After iterations: Level approximation output is placed in the pyramid at level .
- Types of Pyramids (based on filters):
- Mean pyramids (neighborhood averaging)
- Gaussian pyramids (lowpass Gaussian filtering)
- Subsampling pyramids (no filtering)
- Filter can be based on: Nearest, Bilinear, Bicubic.
Upsampling and Downsampling
-
Upsampling:
-
Doubles the spatial dimensions of approximation images.
-
Given a 1D sequence , the upsampled sequence is:
f_{2\uparrow}(n) = \begin{cases} f(n/2) & \text{if } n \text{ is even} \ 0 & \text{otherwise} \end{cases}$$
Insert a 0 after every value in sequence. -
-
Downsampling:
-
Halves the spatial dimensions of the prediction images.
-
Given by:
Discard every other sample.
-