Texture Definition and Analysis
Definition of Texture
Texture is defined as the regular repetition of an element or pattern on a surface.
Purpose of Texture Analysis
- Identify and differentiate: To identify different textured and non-textured regions within an image.
- Classify and segment: To classify or segment different texture regions within an image.
- Extract boundaries: To extract boundaries between major texture regions.
- Describe texel unit: To describe the basic texture element (texel unit).
- 3-D shape from texture: To infer 3-D shape from texture variations.
Texture Regions and Edges
Texture regions can be identified by examining the spatial variations in pixel intensities. Edges between texture regions represent abrupt changes in these spatial patterns.
Texture Classification Process
Typical Flow-chart
A typical texture classification method involves the following steps:
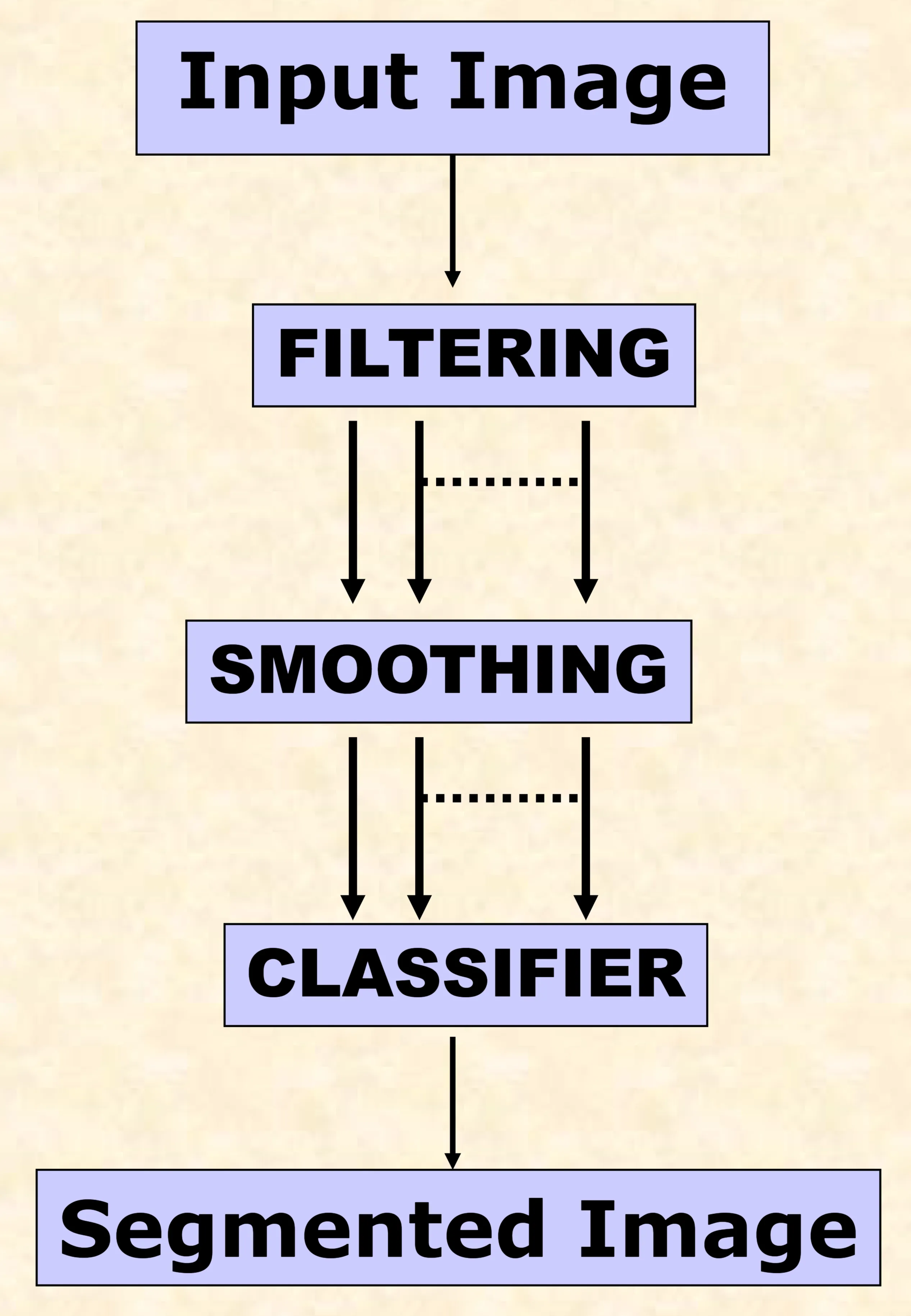
- Input Image: The original image to be analyzed.
- Filtering: Applying filters to enhance texture features.
- Smoothing: Reducing noise and creating a more uniform representation.
- Classifier: Using an algorithm to assign texture labels.
- Segmented Image: The output image with segmented texture regions.
Gabor Filters for Texture Analysis
2-D Gabor Filter
The 2-D Gabor filter is defined as:
Where:
- : spatial spread
- : frequency
- : orientation
Components of Gabor Filter
- Gaussian component: Provides localization in the spatial domain.
- Sinusoidal component: Provides frequency and orientation selectivity.
Properties of Gabor Filters
- Tunable bandpass filter: Can be adjusted to select specific frequencies.
- Similar to STFT: Similar to a Short-Time Fourier Transform or windowed Fourier transform.
- Uncertainty principle: Satisfies the lower-most bound of the time-spectrum resolution.
- Multi-scale, multi-resolution: Analyzes textures at different scales and resolutions.
- Selectivity: Has selectivity for orientation, spectral bandwidth, and spatial extent.
- Human visual cortex: Response is similar to that of the human visual cortex.
- Applications: Used in texture segmentation, iris, face, and fingerprint recognition.
- Computational cost: Often high due to the need for a large filter bank.
Examples of Texture Segmentation Using Gabor Filters
Texture Image Segmentation
Examples demonstrate how Gabor filters can be used to segment images based on texture:

- Texture Image: Input image with different texture regions.
- Magnitude of the Gabor Responses: Shows the strength of the filter responses.
- Smoothed Features: Creates a more uniform representation of the filter responses.
- Initial and Final Classification: Illustrates the process of assigning texture labels and refining the segmentation.
