Illustrate various salient components and functionalities of a video surveillance system with a suitable block diagram stating the roles and scopes of associated computer vision tasks Answer:
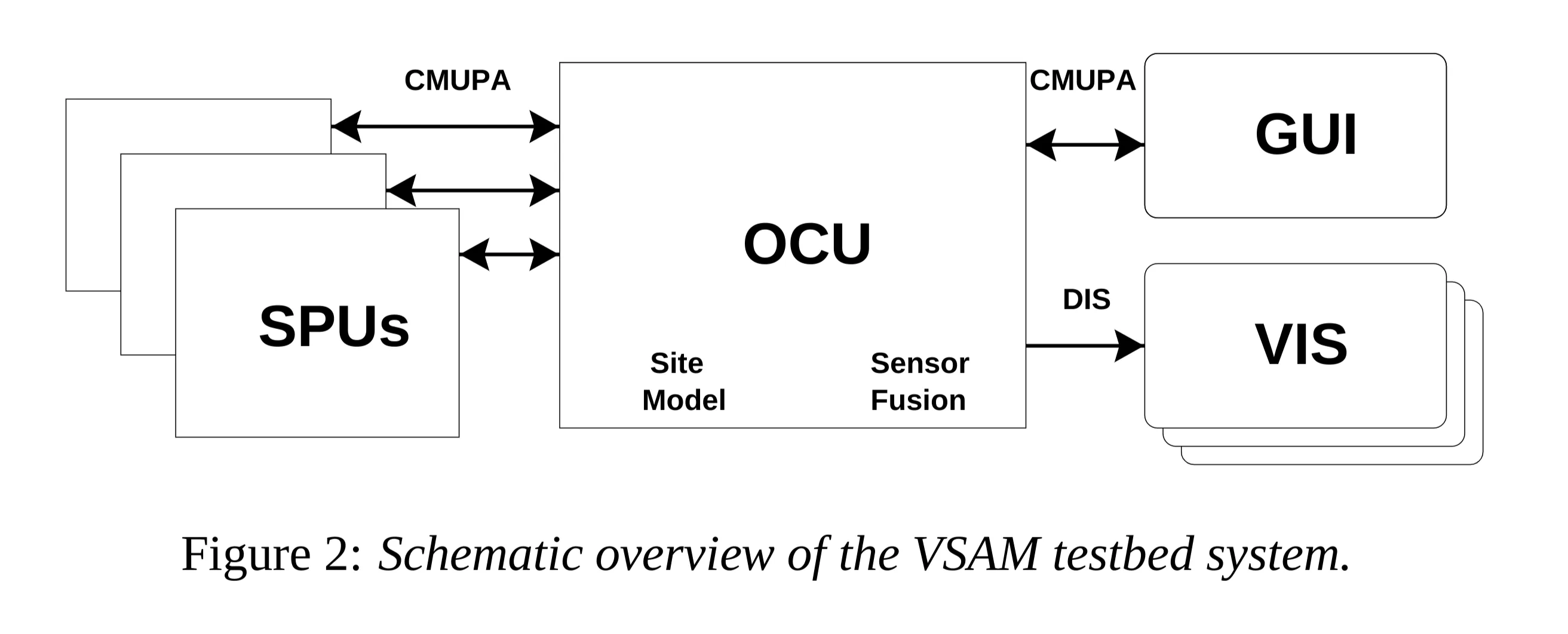 Component Roles and Associated Computer Vision Tasks:
Component Roles and Associated Computer Vision Tasks:
-
Sensors (Cameras - PTZ, Fixed, Thermal, etc.):
- Role: Raw data acquisition (capturing video streams of the environment).
- Scope: Provides the primary input signal. Sensor type (e.g., PTZ, thermal) influences the capabilities and subsequent processing steps.
- Associated CV Tasks: Image Acquisition (inherent function).
-
Sensor Processing Unit (SPU):
- Role: Acts as an intelligent filter. Processes raw video locally to extract meaningful information, reducing bandwidth requirements for the network.
- Scope: Focuses on lower-level vision tasks operating directly on pixel data from one or potentially a few closely coupled sensors.
- Associated CV Tasks:
- Moving Object Detection (MTD): Segmenting moving objects from the background (e.g., using background subtraction, temporal differencing, optical flow analysis). Purpose: Focus attention, initial data reduction.
- Object Tracking (Local): Following detected objects within the sensor’s field of view from frame to frame (e.g., using correlation, Kalman filters). Purpose: Maintain object identity over short durations.
- Feature Extraction: Computing relevant descriptors for detected objects (e.g., shape features like area/moments, color histograms, texture). Purpose: Provide input for classification and matching.
- Initial Object Classification: Assigning preliminary labels (e.g., human, vehicle) based on extracted features (e.g., using trained Neural Networks or LDA). Purpose: Semantic understanding, aids tracking/filtering.
- Image Stabilization: Compensating for camera motion (especially for airborne/mobile sensors). Purpose: Enable robust MTD/tracking on non-static platforms.
-
Operator Control Unit (OCU):
- Role: Central integration and decision-making hub. Fuses information from multiple SPUs, incorporates world knowledge (from Site Model), manages sensor resources, and performs higher-level analysis.
- Scope: Operates primarily on symbolic data received from SPUs, performs scene-level reasoning and coordination.
- Associated CV Tasks:
- Multi-Sensor Data Fusion: Combining object detections and tracks from different SPUs observing the same area or object. Purpose: Improve accuracy, robustness, and coverage.
- Object Geolocation: Determining the 3D position of detected objects in world coordinates (e.g., using ray-casting with Site Model, stereo triangulation). Purpose: Situational awareness, enabling spatial reasoning.
- Trajectory Analysis: Analyzing object paths over longer durations and across multiple sensor views (e.g., smoothing, predicting future position, assessing motion salience/purposefulness for false alarm rejection). Purpose: Understand movement patterns, predict intent.
- Activity Recognition / Event Detection: Identifying complex events or behaviors involving one or more objects (e.g., person entering vehicle, loitering, human rendezvous using spatio-temporal reasoning, Markov models). Purpose: High-level semantic understanding of the scene.
- Sensor Coordination & Tasking: Dynamically allocating sensor resources (e.g., tasking a PTZ camera for handoff or slaving based on OCU analysis and Site Model visibility). Purpose: Optimize sensor usage, maintain track continuity.
-
Site Model Database:
- Role: Stores geo-spatial and semantic information about the environment (e.g., terrain elevation, building locations, road networks, foliage areas).
- Scope: Provides static world context to the OCU.
- Associated CV Tasks: Enables specific CV tasks in the OCU, such as:
- Geolocation (via ray-terrain intersection).
- Visibility Analysis (for sensor tasking).
- Contextual Reasoning (e.g., vehicles expected on roads, suppressing alarms in foliage).
-
Graphical User Interface (GUI) / Visualization:
- Role: Presents fused information, object tracks, trajectories, alerts, and context to the human operator. Allows the operator to task the system and query information.
- Scope: Human-computer interaction layer.
- Associated CV Tasks: Displays the output of the CV tasks performed by SPUs and OCU (e.g., overlaying tracks on maps/video, showing recognized activities).