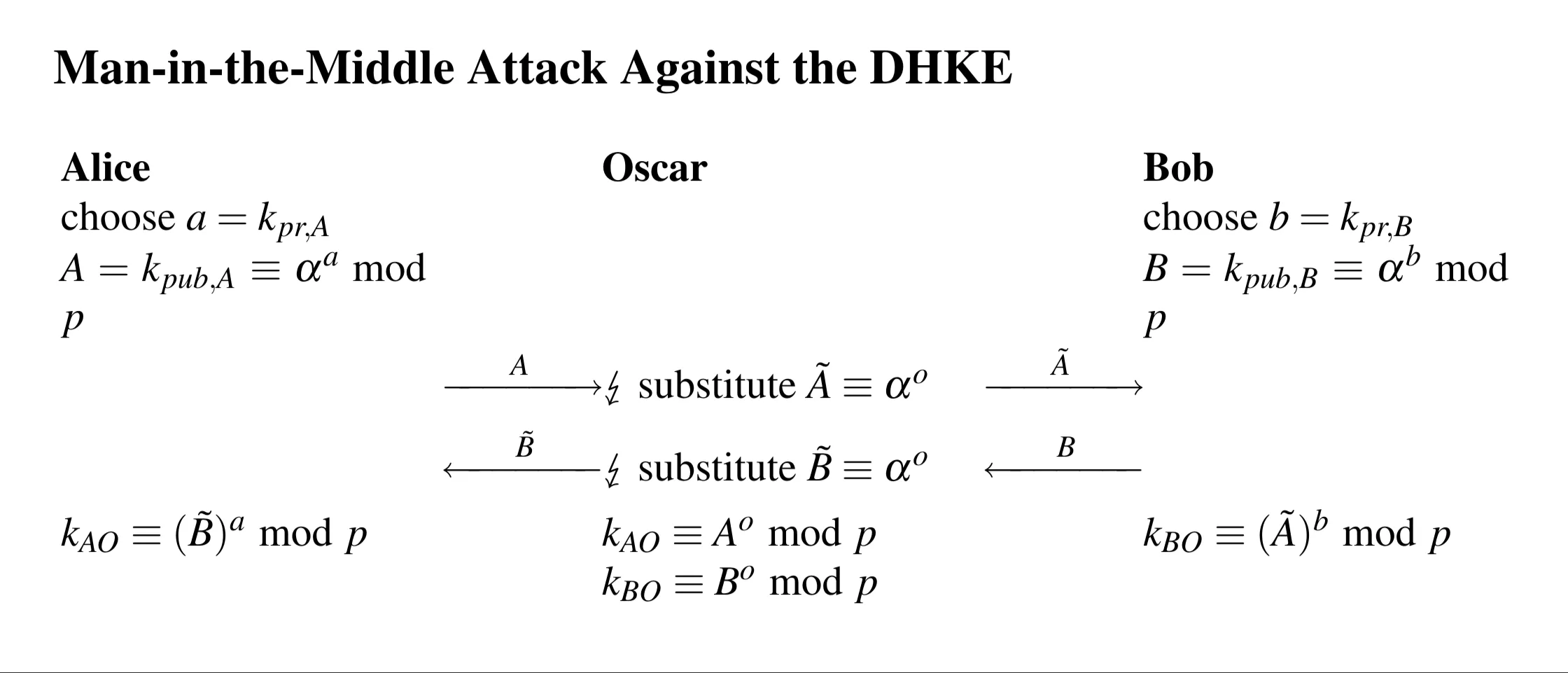
- How does the man in the middle attack occur during the Diffie-Hellman Key Exchange (DHKE) method?
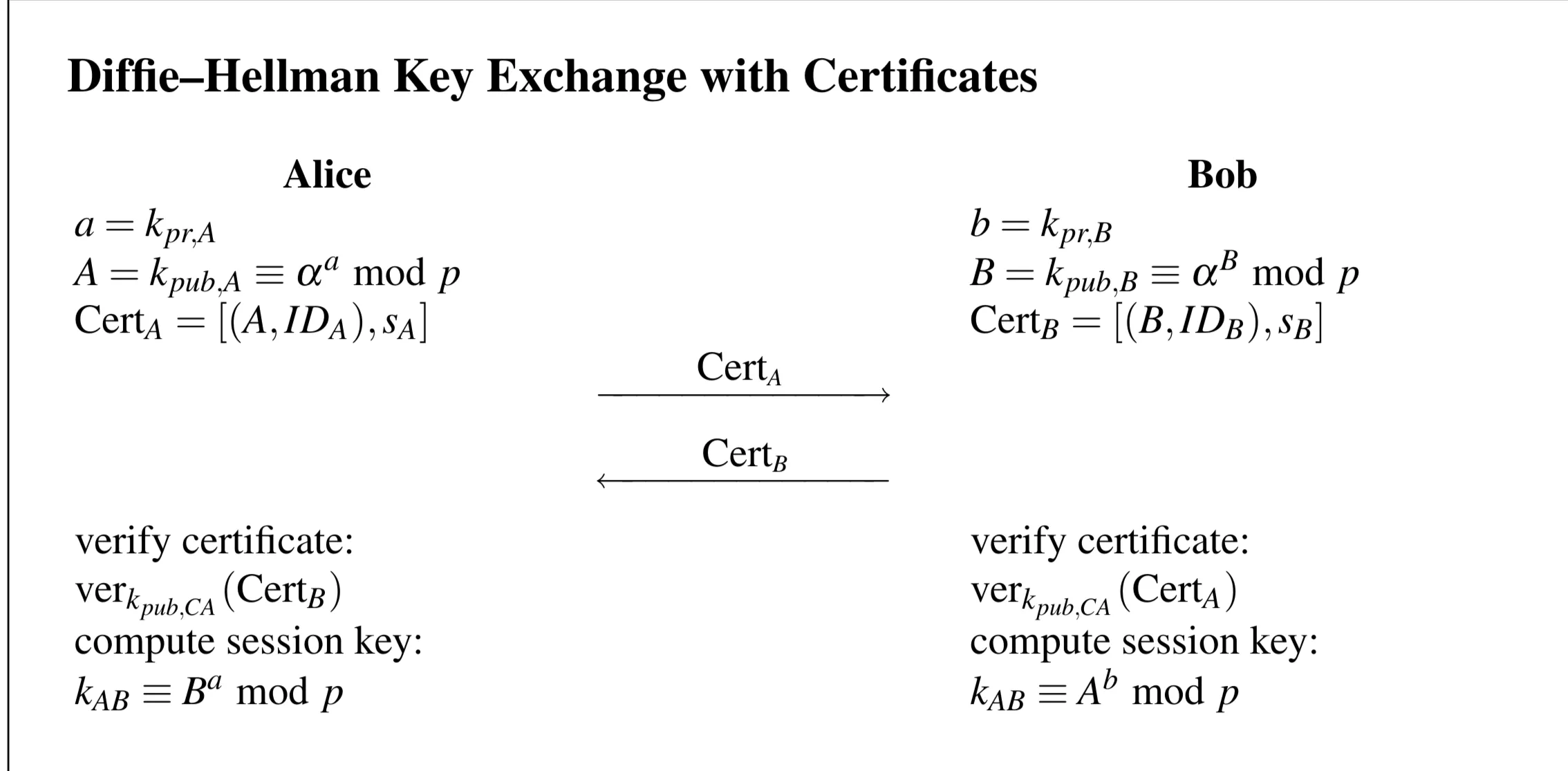
- What is the major drawback of the DHKE method? Show how it can be addressed in the digital certificates.
Transclude of Levels-of-Key-Establishment#d5465c
- *List the content of digital certificates version x.509 and bear use.
X.509
- X.509 Certificates: A standard format for certificates used widely (e.g., in web browsers for HTTPS/SSL/TLS).
Shows typical X.509 fields:
Serial Number: Unique ID for the certificate.Certificate Algorithm: Which signature algorithm the CA used (e.g., RSA with SHA-256).Issuer: Which CA issued this certificate.Period of Validity: “Not Before” and “Not After” dates. Keys/certificates expire!Subject: The identity () of the key owner (person, server name, etc.).Subject's Public Key: The actual public key and its algorithm (e.g., RSA, ECC) and parameters.Signature: The CA’s digital signature covering all the above fields.
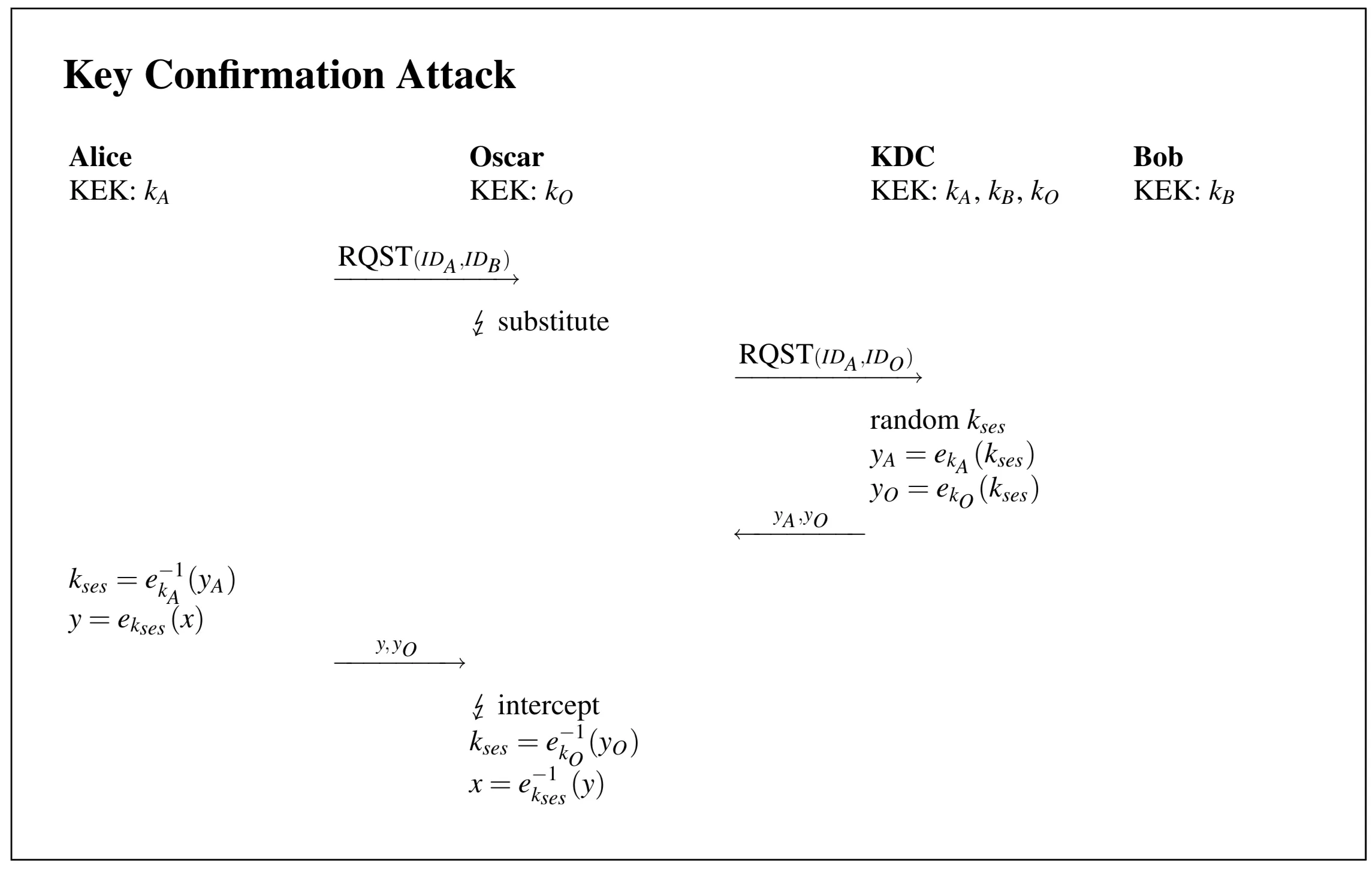
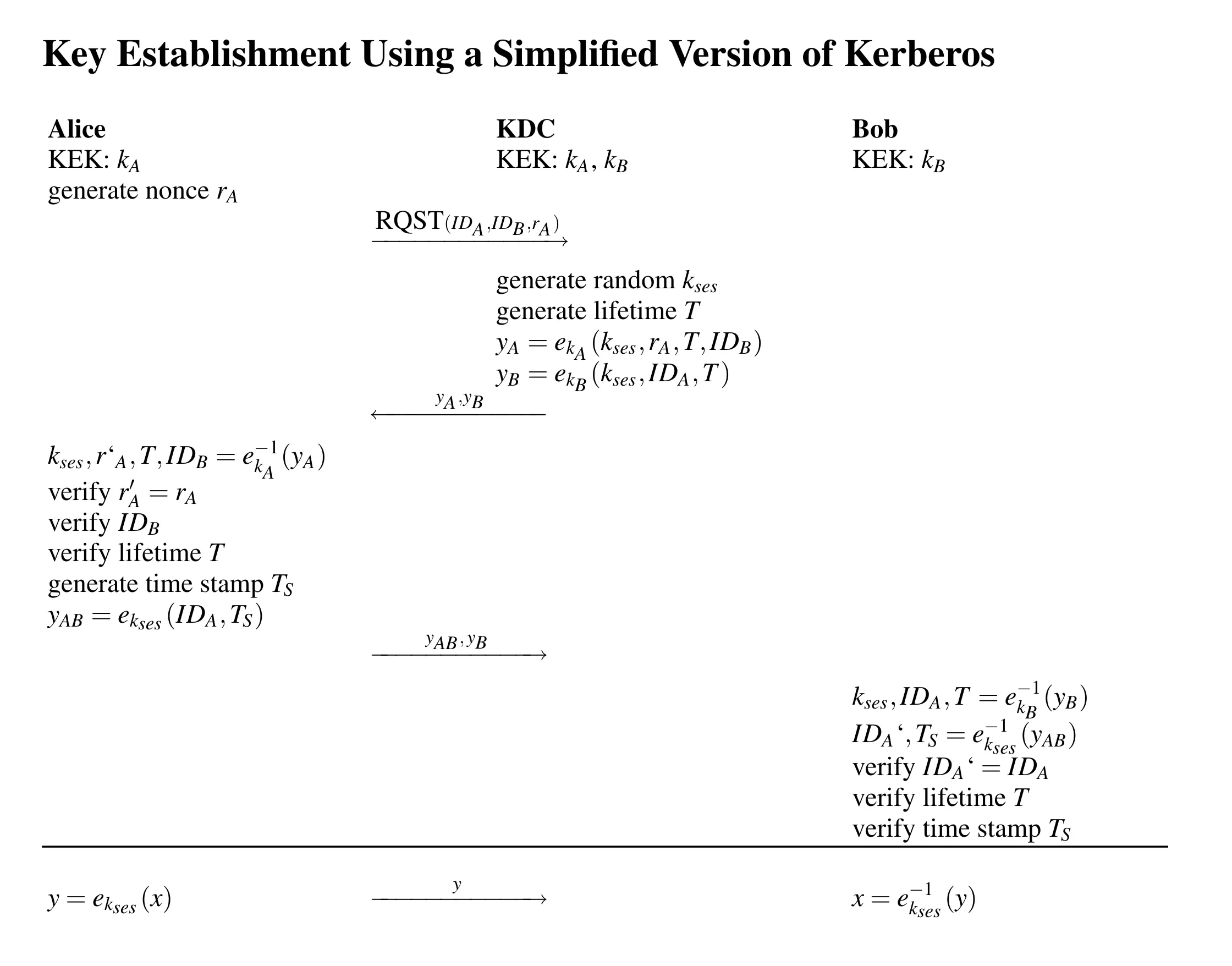
- Illustrate Key confirmation attack and discuss Kerberos Key Exchange Method.