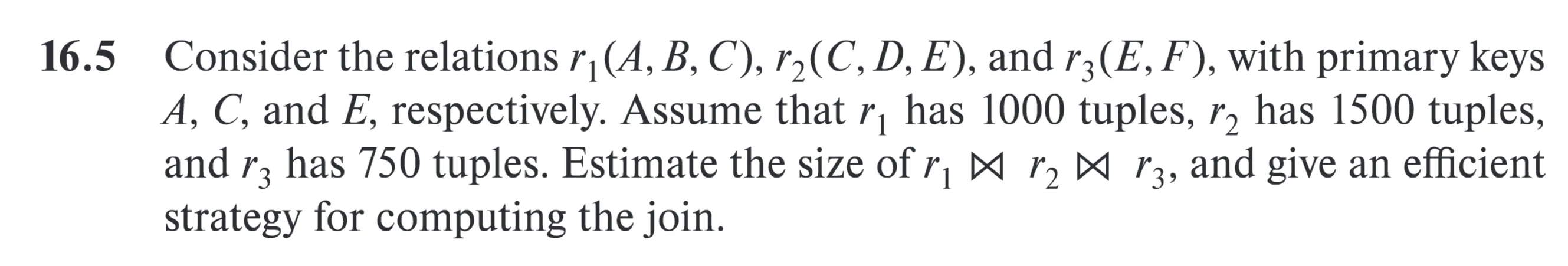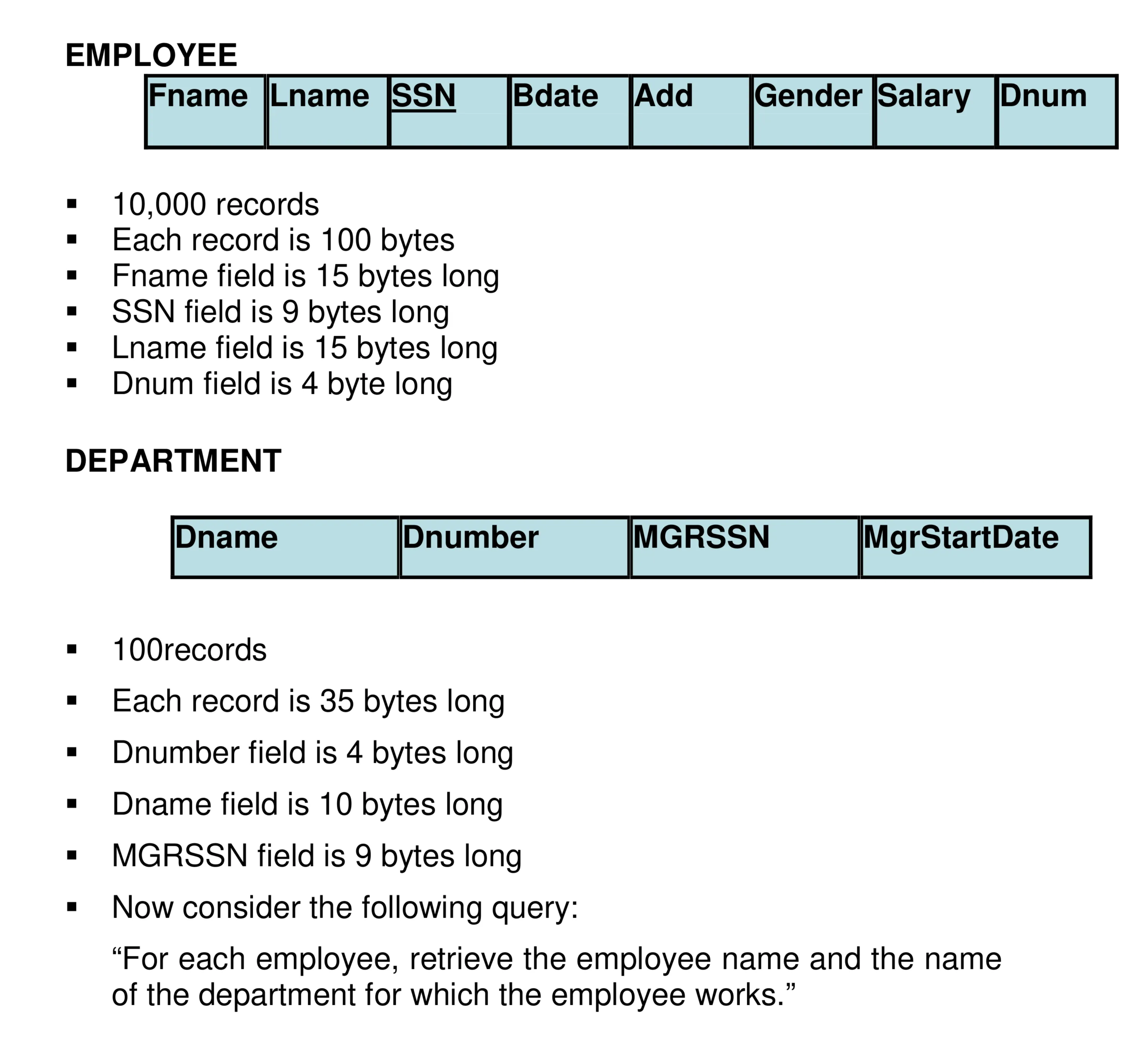
ADBMS formulas
Link to original
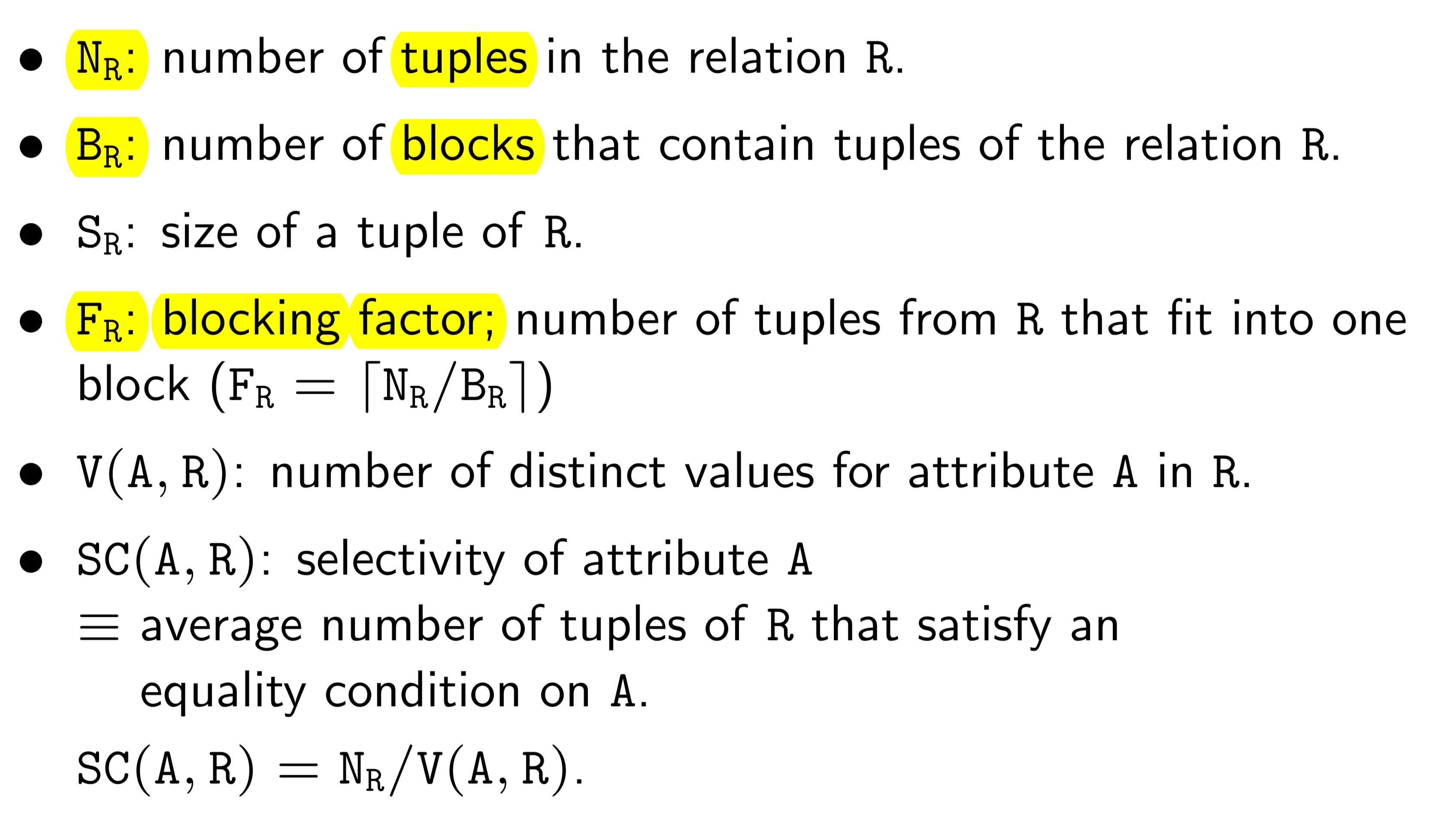
Basic Cost Estimation:
(where b is the number of block transfers, is the time to transfer one block, S is the number of seeks, and is the time for one seek)
Linear Search (A1) - General Case:
Cost = (where is the number of blocks in relation r)
Linear Search (A1) - Selection on Key Attribute:
Cost =
Primary Index, Equality on Key (A2):
Cost = (where is the height of the index)
Primary Index, Equality on Nonkey (A3):
Cost = (where b is the number of blocks containing matching records)
Secondary Index, Equality on Nonkey (A4) - Single Record (Candidate Key):
Cost =
Secondary Index, Equality on Nonkey (A4) - Multiple Records:
Cost = (where n is the number of matching records)
Number of Merge Passes (External Sort-Merge):
(where M is memory size, is buffer block per run and blocks for relation r)
Total Block Transfers (External Sort-Merge):
Total Number of Seeks (External Sort-Merge):
Nested-Loop Join (Worst Case Block Transfers):
(where is the number of tuples in r, is the number of blocks in s, and is number of blocks in r)
Nested-Loop Join (Worst Case Seeks):
Nested-Loop Join (Smaller Relation in Memory):
(block transfers and 2 seeks)
Block Nested-Loop Join (Worst Case):
(block transfers) + (seeks)
Block Nested-Loop Join (Best Case):
(block transfers) + 2 (seeks)
Improved Block Nested-Loop Join:
Cost = (block transfers) + (seeks)
Indexed Nested-Loop Join:
Cost = (where c is the cost of traversing the index and fetching matching tuples)
Merge-Join Cost:
(block transfers) + (seeks) + (cost of sorting if relations are unsorted)
Hash function mapping
maps values to
Partitioning tuples Each tuple is put in partition where . Each tuple is put in partition , where .
Number of Partitions (Hash-Join, Fudge Factor):
(where f is a fudge factor, typically around 1.2)
Number of Passes for Recursive Partitioning (Hash-Join):
Cost of Hash-Join (No Recursive Partitioning):
(block transfers) + (seeks)
Cost of Hash-Join (With Recursive Partitioning):
(block transfers) + (seeks)
Cost of Hash-Join (Build Input in Memory):
B+-Tree Properties (Children): 1. Each node that is not a root or a leaf has between and children.
B+-Tree Properties (Leaf Node Values): 1. A leaf node has between and values.
B+-Tree Properties (Root - Non-Leaf): 1. If the root is not a leaf, it has at least 2 children.
B+-Tree Properties (Root - Leaf): 1. If the root is a leaf, it can have between 0 and values.
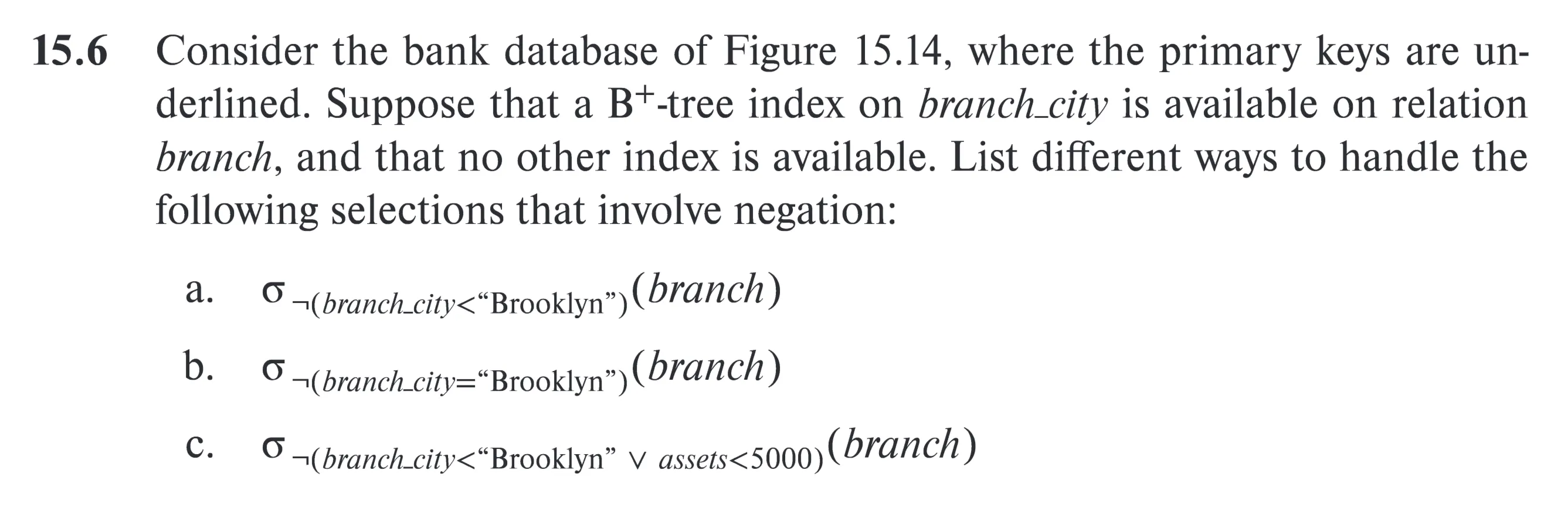
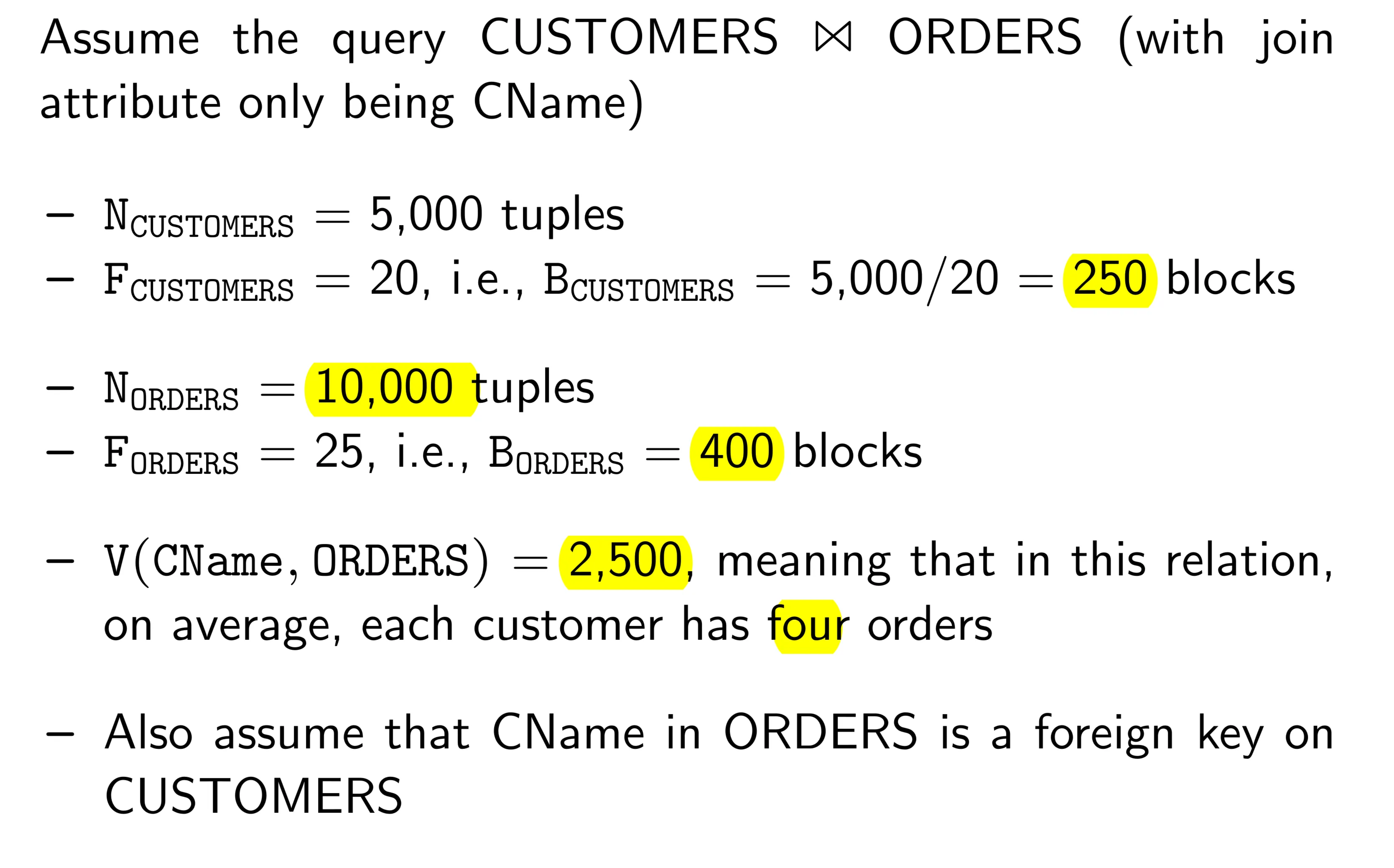
 [[8. Query Processing.pdf#page=24&rect=58,141,533,626|]]
[[8. Query Processing.pdf#page=24&rect=58,141,533,626|]]